20 SPF facts you need to know
6 months ago
When choosing products with SPF, be sure to take into account geolocation, not all creams protect against UVA rays, and a few more facts about SPF that you need to know. Dermatologist-cosmetologist Victoria Britko (Goncharuk) debunks myths and gives advice.
Victoria Britko (Goncharuk) Dermatologist-cosmetologist
Fact #1: Physical and chemical filters work differently

There are two types of filters: physical and chemical. The former create a kind of “screen” on the skin, mechanically reflecting the solar attack. Most often, manufacturers use titanium dioxide (titanium dioxide), zinc oxide (zinc oxide) as physical filters. Chemical filters have a different principle of operation. If you omit all the complex details, they absorb UV radiation, converting it into thermal energy and thereby neutralizing it. Avobenzone (butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane), salicylates (salicilates), cinnamates (cinnamates) are used as chemical filters. Ideally, when the composition of the product has two types of filters.
Fact #2: There are two types of UV radiation
There are three main types of UV radiation: UVA, UVB and UVC. For the skin, it is UVA that is detrimental - it increases the risk of developing cancer, causes burns and pigmentation. UVB rays are not harmful to the skin and are almost completely absorbed by the ozone layer. They pose a danger only to the cornea of \u200b\u200bthe eye. Therefore, high-quality sunglasses provide protection against two types of radiation.
Fact number 3: protection must be selected, taking into account the skin phototype

In dermatology, there is such a thing as erythemal time. It refers to the minimum dose of sun exposure, after which visible redness appears on the skin. This is an individual score.
Its value depends on the phototype, which, according to the classification of the American dermatologist Fitzpatrick, are five: 1 - skin that practically does not tan, often with freckles, characteristic of owners of light eyes and hair; 2 - skin prone to burns, characteristic of people with light or dark blond hair and light eyes; 3 - well-tanned skin, not prone to burns, characteristic of people with dark hair and dark eyes; 4 - the skin tans perfectly, does not burn, is not prone to the appearance of freckles; 5 - very dark skin, never burns - protection from the sun is laid down at the genetic level.
If you are a blue-eyed blonde, most likely we are talking about the first phototype, in which there is a high risk of burns. In this case, you need a cream with the highest level of SPF.
Fact #4: There is a generally accepted formula for calculating the amount of time you can spend in the sun.
In order to calculate the required SPF, you need to know your erythema time at a given temperature in given weather conditions. This figure must be multiplied by the one indicated on the packaging of the protective agent. As a result, you will get time that you can spend in the sun before erythema (redness) or burns appear.
For example, at a temperature of 30 degrees, the erythemal time of a girl with fair skin and blue eyes is about 10 minutes. Accordingly, with SPF 50 protection, she can spend 500 minutes in the sun (10x50SPF = 500). Funds with SPF must be renewed after contact with water.
Fact number 5: when choosing a means of protection, you need to consider geolocation

The sun "does not shine equally for everyone"! Its activity varies by region. In areas closer to the equator, the rays fall at a right angle - their impact is especially dangerous and detrimental to the skin. There you need to use protection higher than what you are used to using (erythema time decreases sharply). The UV index in your region is easy to determine on the nesgori.ru website or using a special smartphone application. In Moscow, for example, it is quite low - about three. In Sydney, very high - ranging from eight to ten. There, in the daytime, it is better not to appear in the sun at all, even with maximum SPF protection.
Fact #6: Sprays need to be dosed correctly
Sprays are distinguished by fine spraying and lie on the skin in a thin layer. It often turns out that when applied, some areas remain undeveloped. Protection is not enough. Sprays are strictly prohibited for use by children and those who have problems with the respiratory system.
Fact #7: There's not too much of a difference between SPF30 and SPF15
SPF is not only a temporary measure. The higher the value of the protection factor, the more sunlight is blocked by the product. But at the same time, the difference between SPF30 and SPF15 is not too big. So SPF15 neutralizes 94% of the sun's rays, SPF30 - 97%, SPF50 -98%.
Fact #8: You don't have to apply SPF beforehand
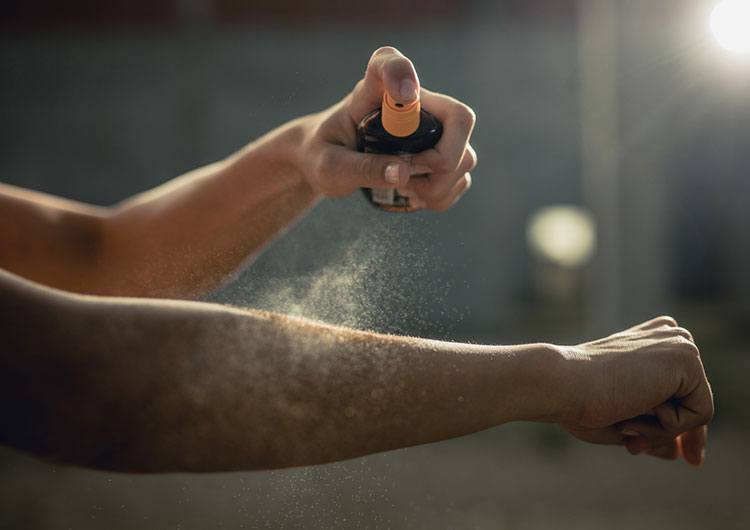

It is not necessary to apply the product 30-60 minutes before sun exposure, as many experts advise. SPF starts working right away! Doing it on the beach is quite appropriate. In the first days of exposure to the active sun, it is better to use products with maximum protection. Further SPF can be reduced. Never start your tan with oils - they don't provide the protection you need. They are good for moisturizing the skin after sunburn. Use shea butter, jojoba, almond, rosehip.
Fact #9: Most day care products already contain SPF
This applies not only to skincare, but also to decorative cosmetics. Most day creams have an SPF of between 15 and 20. This information is listed on the packaging. See composition. Look for ingredients: oxybenzone, sulisobenzone, PABA derivatives, octylmethoxycinnamate, zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, avobenzone.
Fact #10: SPF should also be used on cloudy days
It is a myth that protection is not needed when it is cloudy.
Even when the sun is not visible at all and the sky is overcast, about 40% of UV radiation reaches the earth. This is enough to burn the owners of the first skin phototype.
Even in February, with the “cold” sun, freckles may appear in them.
Fact #11: Using SPF does not cause vitamin D deficiency
In our climate, vitamin D preparations, which are produced by UV exposure, should be taken from September to March (and sometimes during the summer months). Some people are afraid to use creams with SPF, believing that this causes a deficiency of cholecalciferol (vitamin D3). There is no study to prove that this is indeed the case.
Fact #12: SPF in Foundations Lasts About 2 Hours

In tonal foundations, manufacturers most often use SPF from 10 to 20. Do not use them in active sun unless necessary. On the beach, tonal foundations are generally not recommended. Even if you work in an office, before going outside, remove the cream and reapply.
Fact #13: Dark skinned women can use products with a lower SPF
On dark skin, sunburns and age spots appear less often. This does not mean that it should not be protected. It is necessary, but the degree of protection may be lower.
Fact #14: Don't Use Last Season's Sunscreen
Every cosmetic has an expiration date. But for sunscreens, it is no more than a year. Check the expiration dates of all last year's funds. If they run out, feel free to throw the rest in the trash.
Fact #15: SPF Cream Doesn't Guarantee No Freckles

Cosmetologists even have such a concept as a “freckled phototype”. On such skin, under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, melanin is actively formed, which is distributed pointwise. No cream can stop this process 100%.
Fact #16: Skin care ingredients in products with physical filters are useless
In addition to SPF protection, creams may contain caring and moisturizing components: hyaluronic acid, vitamins, essential oils. But in products with physical filters, additional ingredients are useless. Filters create a protective “screen” on the surface of the skin that reflects UV rays and prevents skin care components from penetrating into the skin. If you want to hydrate and nourish, apply your daily serum under your SPF.
Fact #17: Some Ingredients in Protective Products Should Be Avoided
Avoid parabens, strong preservatives and fragrances that can provoke allergies in the composition of protective agents. Benzophenone can cause endocrine disruption. Manufacturers of protective products often use retinyl palmitate. Exposure to UV rays can cause pigmentation. Avoid using cosmetics with retinoids during the period of solar activity.
Fact #18: There is no 100% natural product with SPF in nature

All natural remedies are made from oils. But their maximum SPF is 4 (SPF is considered working from 10). If a larger index is indicated on the package, there are two options: either there are other filters in the composition, or this is a marketing ploy.
Fact #19: UV does not penetrate clothing
Even light fabric is a mechanical barrier to UV rays. Under clothing, the skin does not tan - this is a reliable protection against burns.
Fact #20: Hair also needs UV protection.
Hair needs protection just as much as skin. Under the influence of UV rays, they not only quickly lose color. UV light dries out hair, making it dull and brittle. During the period of solar activity, it is better to use special sprays and oils.
Similar materials from the rubric